Selections
- Abraham and Melchizedek, by 1645, canvas, 100 × 125 cm.Paris, Musée National du Louvre.
- Allegory of Abundance, canvas, 198 × 287 cm.Genua ECR Marchese A. Doria.
- Nativity, 1645, canvas, 398 × 218 cm.Genua, S. Luca.
- Nativity, copper, 38 x 30 cm.Genua, Galleria Balbi.
- Homecoming Jacob, canvas, 99 × 123 cm.Madrid, Museo del Prado.
- St. Bernard and the crucifix, canvas, 305 × 222 cm.Sampierdarena ( near Genoa ), S. Maria della Cella.
- St. Jacobus breaks the walls, canvas, 316 × 327 cm.Genua, Oratorio di S. Giacomo Maggiore Apostolo.
- Noah lets the animals out of the ark, screen, 198 × 216 cm.Wien, Kunsthistorisches Museum.
- Rebecca’s repatriation to Jaacob to Canaan, canvas, 191 x 280 cm., Former Rothschild Collection, Priv Collection Granados, Madrid.
- Expulsion of merchants and changers from the temple, canvas, 98 × 120 cm.Paris, Musée National du Louvre.
- Vulcan and Juno, canvas, 198 × 294 cm.Genua ECR Marchese A. Doria.
Life
The pupil Giovanni Battista Paggis, Giovanni Andrea De Ferrari and Anthony van Dyck, nor was formed in Rome, Florence, Parma and Venice and then entered the service of Duke Charles I in Mantua.
Castiglione has especially gained its reputation for its excellent representations of animals, which he understood both show off and after close observation in the respective posture, as well as in the subject corresponding view;
the historical and biblical allegations usually only maintain the theme for his paintings to give away, while animals and the landscape artistic play the main role.
A large part of his work in oil painting dedicated to the world of the Old Testament, specifically the story of Abraham and the patriarchs.
Particular examples such as » The repatriation of Rebecca in the caravan » he took occasion to be able to bring his downright ingenious animal painting to advantage here.
He treated his narrative, often biblical representations often in similar construction manner, his characters follow conventional models;
In his view color he follows, both Italian and Dutch models of animal painting.
Castiglione has become very well known as an etcher, with his etchings follow the style of the already world famous Rembrandt;
It has more than 70 such sheets.
1786 appeared to Venice a sequence of twelve after Castiglione’s drawings of G. Zompini etched sheets, the engraver the magnificent sketches Castiglione did not understand reproduce.
The British consul in Venice, Joseph Smith had purchased the mid-18th century, a collection of over two hundred drawings, in part from the part of the collection of the Dukes of Mantua, who was auctioned in 1711 in Venice.
The volumes were in the Royal Collection at Windsor Castle.
Life
The pupil Giovanni Battista Paggis , Giovanni Andrea De Ferraris (1598–1669) and Anthony van Dycks educated himself in Rome, Florence, Parma and Venice and then entered the service of Duke Charles I in Mantua.
Castiglione has achieved his reputation through his outstanding depictions of animals, which, after careful observation, he was able to demonstrate both in the respective posture and in the gaze corresponding to the subject; the historical and biblical allegations usually only give the theme for his pictures, while animals and the landscape play the main artistic role. Much of his oil painting work is devoted to the themes of the Old Testament, namely the story of Abraham and the tribal fathers. In particular, he took examples such as Rebecca’s home tour in the caravan as an opportunity to showcase his genuinely ingenious animal painting.
He often treated his narrative, often biblical representations in a similar way, his characters follow conventional models; in his conception of color he follows both Italian and Dutch models of animal painting. Castiglione has also become very well known as an etcher, with his etchings following the style of Rembrandt , who was already world-famous at the time ; There are over 70 such sheets. In 1786 a series of twelve sheets etched after Castiglione’s drawings by G. Zompini was published in Venice, although the engraver did not know how to reproduce Castiglione’s grandiose preliminary drawings.
The British consul in Venice, Joseph Smith , had acquired a collection of more than two hundred drawings in the mid-18th century, some of them from the part of the collection of the Dukes of Mantua that was auctioned in Venice in 1711. The volumes went to the Royal Collection at Windsor Castle .
биография
Архитектурное каприччио с вакханальной процессией Филиппо Гальярди и Джованни Бенедетто Кастильоне
Кастильоне родился в Генуе. Его ранняя подготовка неясна. Возможно, он учился с Синибальдо Скорца. Витткауэр описывает его как «страстного ученика» Энтони ван Дейк, прибывший в 1621 г., и Питер Пауль Рубенс, жившие в городе в первом десятилетии XVII века и чьи картины были там легко доступны. Возможно, он тренировался у генуэзцев. Бернардо Строцци. Он жил в Риме с 1634 по 1645 год, затем вернулся в Геную. Он также ездил в Флоренция и Неаполь. Он вернулся в Рим в 1647 году, а затем переехал в 1651 году, чтобы стать придворным художником в Мантуе. Герцог Карло II и его жена Изабелла Кьяра де Австрия. Он умер в Мантуе.
За свою жизнь у него были разные прикосновения к закону. Королевская галерея в Лондоне, где в 2013 году проходила выставка его работ, сделала следующее заявление: «Джованни Бенедетто Кастильоне также был жестоким и вспыльчивым человеком, который неоднократно предстал перед судом за нападения, якобы пытался сбросить свою сестру с лица земли. Крыша и был вынужден покинуть Рим, вероятно, после совершения убийства. Волнения, которые характеризовали его жизнь, омрачили его художественный талант, и Кастильоне изо всех сил пытался добиться признания при жизни. Многое из того, что известно о художнике, получено не из выполненных заказов, а из судебных документов «.
Biography of Giovanni Benedetto Castiglione
Castiglione was born in Genoa and was baptized on 23 March 1609. Little is known about the early period of his life, and researchers can only guess who he studied with. They were probably local landscape painters and caravaggist Bernardo Strozzi. The artist’s work traces the influence of Pieter Paul Rubens and Antoon van Dyck the latter he could meet in person.
Giovanni Castiglione was admitted to the Academy of Saint Luke in 1632. He lived in Rome for about 15 years, studied the works of the High Renaissance masters and prominent contemporaries. From Nicolas Poussin, for example, he adopted the art of constructing complex and carefully organized compositions. In the early 1640s, the artist returned to Genoa and carried out several important orders for the decoration of church altars. Later, the images he created had a noticeable impact on the local school. Around the same time, he creates the first works in the technique of monotype. It is Castiglione who is considered the inventor of this type of printed graphics.
 Angel Who Is the Shepherd
Angel Who Is the Shepherd
From 1647 to 1652, the artist again lived in Rome
He was influenced by the most popular painters at that time Salvator Rosa and Giovanni Lorenzo Bernini. The master’s style becomes more emotional and dramatic. At the same time he studied engravings by Rembrandt (Rembrandt Harmensz van Rijn) and adopted many techniques. For the virtuoso image of chiaroscuro on the etchings, the author was even nicknamed the second Rembrandt. He also earned the nickname Grechetto for his classic pastoral scenes.
In later years, Castiglione was in great demand and often visited the largest Italian cities. He became the court painter of the Gonzaga family in Mantua, and also visited Naples, Venice, Parma and his native Genoa. Many of the master’s works were created in the studio together with his brother Salvatore and his son Francesco, which creates difficulties in attribution. Castiglione died on May 5, 1664 in Mantua and was buried in the local cathedral. His son became the new court painter.
 Family with cattle in the background of the landscape
Family with cattle in the background of the landscape
Giovanni Castiglione gained international fame during his lifetime. In the 18th century, he was still imitated, and his works were copied as classics. For example, oriental and “witchcraft” motifs from his engravings come to life in the work of Giovanni Battista Tiepolo. But in the 19th century, the popularity of this author faded away and they began to forget him. Much information has been lost.
It is curious that not only records of completed orders help to restore the facts, but also court documents. Apparently, the artist was distinguished by a quick-tempered disposition and repeatedly became a participant in the riots, which complicated the development of his career. Currently, the work of the master is appreciated, and his works are kept in the best museums in Italy, in the Louvre, the Hermitage and other famous collections.
The most famous paintings by Giovanni Castiglione
The paintings of Giovanni Castiglione testify to him as a brilliant draftsman and master of composition. Another advantage is its innovation and ingenuity. He came up with a monotype, was the first to paint in oil on paper and used cinnabar, which no one used at that time. Among the famous works of the author are the following:
- “Before Noah’s Ark” (about 1650). The author loved to paint a variety of animals and turned to the plot with Noah’s ark throughout his entire creative career.
- Diogenes in Search of Man (c. 1650). The plot is taken from a fable in which Diogenes wandered around Athens with a lamp and said that he was trying to find an honest man. The idol, satyr, animals and bones in the picture are evidence of the depravity and decline of society.
- Saint Francis in ecstasy (c. 1650). This work was painted in Rome, probably as an altarpiece. Skull, book and cross are symbols of worldly vanity and eternity of the spiritual world.
- “The head of a man in an oriental headdress” (1655). The artist created a whole series of works in monotype technique with exotic portraits of men and women. It became popular and was reproduced frequently.
 Head of a bearded Oriental
Head of a bearded Oriental Holy Family with little Saint John the Baptist
Holy Family with little Saint John the Baptist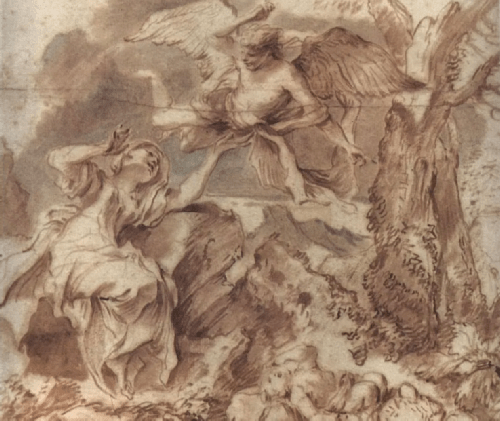 Hagar in the desert
Hagar in the desert
Приложения
Библиография
- В эту статью включены выдержки из словаря Булье . Это указание можно удалить, если текст отражает текущие знания по данной теме, если цитируются источники, если он соответствует текущим языковым требованиям и не содержит слов, противоречащих правилам. Нейтральность Википедии.
- (ru) Гений Кастильоне , 1648 г.
- (nl) Корнелис де Би , Кабинет Het Gulden , 1662, стр. 305
- (de) Zur Problematik der Rembrandt-Rezeption im Werk des Genuesen Giovanni Benedetto Castiglione, (Genua 1609-1664 Mantua) , 2004 г.
- (it) П. Беллини, L’opera incisa di Giovanni Benedetto Castiglione , 1982, изд. Ripartizione cultura e spettacolo, Милан
- (fr) Э. Бенезит, Критический и документальный словарь художников, скульпторов, дизайнеров и граверов , с. 589-590, 1976, Париж, изд. Книжный магазин Gründ, Том II
- (it) Дж. Диллон, Il genio di Giovanni Benedetto Castiglione, Il Grechetto , 1990, изд. Сагеп, Генуя
- (fr) Мишель Лаклотт, Жан-Пьер Кузен и Арно Пьер, Словарь живописи , изд. Ларусс
- (en) Липманн, гравюра и офорт , 1906, Нью-Йорк
- (en) Maberly, The Print Collector , 1880, Нью-Йорк,
- (it) Сопрани, Le Vite de ‘pittori genovesi , 1768, Генуя
- (де) Тиме-Беккер, Allgemeines Lexikon der Bildenden Künstler von der Antike bis zur Gegenwart , стр. 164-166, 1912, Лепизиг, т. 6
- (en) Рудольф Витткавер , Искусство и архитектура Италии, 1600-1750 , стр. 353–355, 1993, История искусства «Пеликан», изд. Книги о пингвинах
- (де) Курт Цайтлер (под руководством), Верке фон и ум Джованни Бенедетто Кастильоне (1609-1664) , 2004, изд. Staatliche Graphische Sammlung, Мюнхен
- (fr) Ларусс, Универсальный словарь , Париж, 1877 г.
- Клод-Жан Дармон , «Сухая игла и гравюра Мастера 1615 года в Кастильоне в Италии» , в журнале Azart , № 38, май-Июнь 2009 г..
Works
Castiglione was a brilliant draftsman and pioneered the development of the oil sketch (often using a mixture of mediums) as a finished work — previously they had been used only for working studies for another finished piece, for example by Rubens. He returned to the same subjects over and over again, as both paintings and etchings, but with significantly different compositions each time.
He also executed some sixty etchings, arguably the most famous of which is The Genius of Castiglione, published by Giovanni Giacomo de Rossi in 1648. Diogenes searching for a Man is another of the principal of these; others are about religious themes. Some are moralistic stories such as that of the blind leading the blind. The etchings are remarkable for light and shade, and have even earned for Castiglione the name of a second Rembrandt. He was exposed to Rembrandt’s etching by 1630.
In about 1648 he invented the monotype, the only printmaking technique to be an Italian invention, making over twenty over the succeeding years. His most popular and influential prints were a series of exotic heads, mostly of vaguely Oriental males, but also of women. These were produced in great numbers. Among the subjects of his etchings are Diogenes with his lantern, Noah leading animals into Arc, St Joseph Asleep during Flight from Egypt, Circe surrounded by animals, Silenus at the fountain, Nativity, Resurrection of Lazarus, and The Genius of Castiglione.

Giovanni Benedetto Castiglione — The Adoration of the Shepherds, Louvre
Castiglione was famous for his ability to paint animals, mostly farm animals, and they were often a dominant motif in his paintings. For example, in the painting of Jesus clearing the temple of Moneylenders, the religious event is a minor, background part of the painting, the stampede of animals is far more prominent than the scattering of bankers. Castiglione’s attention to detail in the depiction of nature is regarded as proof of the influence of Scorza and the Flemish still life and animal painter Jan Roos who was a long-term resident of Genoa. It has been suggested that it was Jan Roos who convinced Castiglione to enliven his religious and mythological compositions with animal and still life elements.
In Mantua, he received his name of Grechetto, from the classic air of his pastoral depictions. In his later years, he was severely afflicted by gout. His brother Salvatore and his son Francesco excelled in the same subjects; and it is thought that many paintings which are ascribed to Benedetto are only copies after him, or perhaps originals by his son or brother. He also influenced Anton Maria Vassallo (c1640-60). Among those who engraved after him were Giovanni Lorenzo Bertolotto in Genoa, the Venetian Anton Maria Zanetti, Michele l’Asne, Louis de Chatillon, and Coreneille Coemans.
His paintings are to be found in Rome, Venice, Naples, Florence, and more especially Genoa and Mantua. The Presepio (Nativity of Jesus) for the church of San Luca, Genoa, ranks among his most celebrated paintings, and the Louvre contains eight characteristic examples. He painted a SS. Mary Magdalene and Catharine for the church of the Madonna di Castello and St. James defeats the Moors for the Oratorio di San Giacomo della Marina, both in Genoa.
КАСТИЛЬОНЕ Джованни Бенедетто
Страница 1 из 2
КАСТИЛЬОНЕ Джованни Бенедетто (1609–1665 гг.) – итальянский художник, талантливый рисовальщик и гравёр, представитель генуэзской школы. В XVIII в. его влияние испытали Себастьяно Риччи (1659–1734 гг.) и Джованни Баттиста Тьеполо (1696–1770 гг.), а также Франсуа Буше (1703–1770 гг.) и Жан-Оноре Фрагонар (1732–1806 гг.). С исторической точки зрения Джованни Кастильоне – значительная фигура для той эпохи, когда особую роль в итальянском искусстве играли фламандские и голландские художники. Приверженец барокко, он использует все его возможности: от простой виртуозности приходит к необыкновенной живости воображения как в сценах сельской жизни, так и в произведениях религиозных. Сначала учился у Дж. Б. Паджи, а затем у Дж. А. де Феррари, а также у Ван Дейка (1599–1641 гг.) во время его второго пребывания в Генуе в 1621–1627 гг., у Бернардо Строцци (около 1581 – 1644 гг.) и Доменико Фетти (около 1589 – 1623 гг.); впервые применил технику монотипии. Однако его раннее творчество больше тяготеет к фламандской жанровой живописи, в особенности к работам ученика Франса Снейдерса (1579–1657 гг.) Яна Роса (в Генуе в 1614–1638 гг.), заимствовав у него тип композиции с изображением животных и различной домашней утвари, которую трактует более широко (в отличие от С. Скорца), напоминая Питера Артсена (1508–1575 гг.) и Иоахима Бейкелара (1530–1573 гг.). Творчество Якопо Бассано (1510–1592 гг.) также должно было произвести на него впечатление
Сторонник северного натурализма, Джованни Кастильоне уделяет особое внимание анималистическим сценам, включённым в картины на библейские сюжеты, к которым он будет обращаться на протяжении всего своего творчества (библейские сюжеты – основные темы картин художника). Через северных художников он приобщается к караваджизму
Впрочем, на протяжении всей жизни источником обновления остаётся для Кастильоне Рембрандт Харменс ван Рейн (1606–1669 гг.), особенно в области графики (его мастерство гравёра снискало ему славу второго Рембрандта). В 1632 г. Кастильоне покидает Геную и отправляется в Рим, где он был два раза (1632–1635 и 1647–1651 гг.). Вероятно (между годами в Риме) он посетил Неаполь, где его имя упоминается в 1635 г., а также другие итальянские города, в частности Геную (около 1645 г.). В период первого пребывания в Риме он поддерживает связь с кругом Николя Пуссена (1594–1665 гг.) и Кассиано даль Поццо (1588–1657 гг.); его манера близка стилю Пьетро Тесты и Пьера Франческо Молы, которые в те годы жили в Риме. В это время он отходит от фламандского искусства и становится сторонником пуссеновского венецианизма, заимствуя у французского художника вакхические и элегические темы. Его репертуар расширяется, стиль становится более упорядоченным, цветовая гамма – более тёплой, композиция упрощается, а рисунок приобретает всё большую свободу. Художник разрабатывает технику масляной живописи на бумаге, унаследованную, по всей вероятности, от фламандцев и венецианцев, позволяющая Кастильоне использовать такие цвета, как киноварь, которые в те годы никто, кроме него, не использовал; изобретает технику монотипии, заключающуюся в создании оттиска при помощи пластинки, на которую чернилами нанесён рисунок.
<< Первая < Предыдущая 1 Следующая > Последняя >>
literature
- Regina Erbentraut: Castiglione, Giovanni Benedetto . In: General Artist Lexicon . The visual artists of all times and peoples (AKL). Volume 17, Saur, Munich a. a. 1997, ISBN 3-598-22757-4 , pp. 223-225.
- Kurt Zeitler, works by and around Giovanni Benedetto Castiglione (1609 — 1664) . Exhibition of the State Graphical Collection Munich in the Pinakothek der Moderne March 12 — April 28, 2004 Munich: State Graph. Collection, 2004 ISBN 3-927803-40-5
- Frances Vivian, The Consul Smith Collection: Masterpieces of Italian Drawing from the Royal Library, Windsor Castle. From Raffael to Canaletto Hirmer, Munich 1989, ISBN 3-7774-5120-7 .
- Franz Röhn, The graphic of Giovanni Benedetto Castiglione , Gebrüder Hoffmann, Charlottenburg, 1932, , OCLC , (Inaugural dissertation of the Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität zu Berlin 1928, 1 volume, 72 sheets, 8 °).
Works
(Selection)
- Abraham and Melchizedek, after 1645, canvas, 100 × 125 cm, Paris, Musée National du Louvre.
- Allegory of Abundance, canvas, 198 × 287 cm. Genoa, Marchese A. Doria collection.
- Christ drives the moneylenders out of the temple
- The fable of Diogenes
- Nativity, 1645, canvas, 398 × 218 cm. Genoa, S. Luca.
- Nativity, copper, 38 × 30 cm. Genoa, Galleria Balbi.
- Homecoming of Jacob, canvas, 99 × 123 cm, Madrid, Museo del Prado.
- St. Bernard and the crucifix, canvas, 305 × 222 cm, Samierdarena (near Genoa), S. Maria della Cella.
- St. Jacobus bursts the walls, canvas, 316 × 327 cm. Genoa, Oratorio di S. Giacomo Maggiore Apostolo.
- Isaac and Rebecca
- Noah lets the animals out of the ark, canvas, 198 × 216 cm, Vienna, Kunsthistorisches Museum.
- Rebecca’s home tour to Jaacob in Canaan, canvas, 191 × 280 cm, former Rothschild collection, Granados private collection, Madrid.
- Expulsion of dealers and money changers from the temple, canvas, 98 × 120 cm, Paris, Musée National du Louvre.
- Vulkan und Juno, canvas, 198 × 294 cm. Genoa, Marchese A. Doria collection.
- The miracle of Soriano
Биография
Он обучался в мастерских Джованни Баттиста Паджи , Джованни Андреа Де Феррари и Синибальдо Скорца в своем родном городе, где недавно останавливался Антон ван Дейк .
Он сразу же специализировался на анималистических картинах под влиянием стиля Скорца. Некоторые критики ссылаются на эту первую фазу . Вход животных в ковчег Академии Лигустика и Ной заставляет животных войти в ковчег Уффици
В 1632 году он переехал со своим братом Сальваторе в Рим , как это задокументировано в настроениях прихода Сант — Андреа делле Фратте . Он стал признанным художником: он был принят в Академию Сан-Лука (1634 г.) и начал часто посещать таких художников, как Джан Лоренцо Бернини , Маттиа Прети и Пьетро да Кортона .
После пребывания в Неаполе он вернулся в Геную, где посвятил себя важным заказам как для галерей генуэзской аристократии, так и для религиозных учреждений. В 1645 году он подписал запрестольный образ с Рождеством для церкви Сан-Лука , считающийся одним из его высших достижений, и снова для своего города он написал Видение св. Бернардо для Санта-Мария-делла-Челла и Сан-Джакомо, прогоняющий мавров для молельни Сан-Джакомо-делла-Марина . В те же годы он начал плодотворное графическое производство, сюжеты которого часто ссылаются на археологические декорации Пуссена , оживляемые фантастическими фигурами сатиров и нимф .
Второе пребывание в Риме датируется примерно 1650 годом, когда был заказан алтарь с изображением Непорочного зачатия, которым поклонялись святые Франциск и Антоний Падуанский , написанный в 1649-1650 годах для капуцинской церкви Осимо , в Марке, сегодня в Миннеаполисский институт искусств Миннеаполиса
Его мастерская, всегда в общении с его братом и сыном Франческо (1641-1716), специализировалась на натюрмортах, библейских и мифологических сценах, всегда переполненных животными. Его тонкие и острые мазки несут в себе неугомонный характер художника, ищущего новые пространственные и формальные решения. Сегодня трудно точно определить, какие работы принадлежат ему, а какие — его брату Сальваторе (1620-1676) и сыну Франческо: надо думать о творчестве этого выдающегося художника как о мастерской, где каждый из трех обогатил другие новыми стимулами и стилистическими решениями. Он также был уважаемым гравером, специализирующимся на технике гравюры и изобретателем техники монотипии : вероятно, его гравюры также повлияли на творчество Рембрандта .
С 1651 года он находился в Мантуе , где стал придворным художником Гонзага . Он также часто останавливался в Неаполе , Парме и Венеции . Видение св. Доменико ди Сориано из церкви Санта-Мария-ди-Кастелло считается одной из последних работ, выполненных для его родного города. Он умер в Мантуе и был похоронен в соборе до 1665 года, дата указана на надгробии. Слева от входа в баптистерий самого собора его изображает лепной медальон с надписью, которая со всем акцентом XVII века заверяет: «Может быть, возродится искусство живописи, умершее вместе с вами. Но после того, как вы , Кастильоне, она всегда будет ниже». Его сын Франческо сменил его на посту придворного художника Фердинандо Карло Гонзага . Он был учителем Джованни Лоренцо Бертолотто , который был в его мастерской с начала 1661 года по март 1663 года.
Biography
 Circe changing the companions of Ulysses into beasts, etching, 1650-51
Circe changing the companions of Ulysses into beasts, etching, 1650-51
Castiglione was born in Genoa. The biographer of Genoese painters, Raffaele Soprani says his parents had him places in the studio of Giovanni Battista Paggi. Wittkower describes him as a «passionate student» of Anthony van Dyck, who arrived in 1621, and Peter Paul Rubens, who stayed in the city in the first decade of the 17th century and whose paintings were readily accessible there. He may have trained under the Genoese Bernardo Strozzi. He lived in Rome from 1634 to about 1645, then returned to Genoa. He also traveled to Florence and Naples. He was back in Rome in 1647, before moving in 1651 to be a court artist in Mantua for Duke Carlo II and his wife Isabella Chiara de Austria. He died in Mantua.
He had various brushes with the law in his lifetime. The Queen’s Gallery in London, where an exhibition of his work was held in 2013, made the following statement: «Giovanni Benedetto Castiglione was also a violent and impetuous man, who was repeatedly in court for assault, allegedly attempted to throw his sister off a roof and was forced to leave Rome, probably after committing murder. The turbulence that characterised his life overshadowed his artistic brilliance, and Castiglione struggled to achieve recognition in his lifetime. Much of what is known about the artist is derived not from fulfilled commissions, but from court documents.»